How GIS Can Compliment GPS And Take Mapping Solutions In Logistics And Transportation To A Whole New Level
Two factors are vital in logistics and transportation regarding maps in use. First, they must provide access to accurate real-time positioning information. Logistics companies must know where the cargo is at any point to avoid delays and ensure customer satisfaction. Second, maps must be informative. For example, access to current traffic congestion can help build more efficient routes.
GIS (Geographic Information System) is one of the technologies making using these features in software possible. It can capture, store, and display tons of valuable data related to positions in space. Today, we’ll consider how it works and highlight some benefits it can bring to companies working in logistics and transportation.
What is GIS, and How Does It Differ From GPS?
Often, when we speak of the necessity to build a real-time map application, the first thing that comes to mind is GPS. Since both GPS and GIS serve a similar purpose and their names look pretty much the same, it makes sense to highlight their main features. Drawing the line between these technologies will help to understand how to build the most optimal software solution for your logistics and transportation business.
GPS, or Global Positioning System, is a satellite-based navigation technology that allows users to determine their precise location and track their movements in real time. All satellites have atomic clocks and transmit signals simultaneously. The GPS receiver, in its turn, can calculate the current position by estimating the distance between the user and at least four satellites which data it receives. It’s a rather complicated principle of operation, we must say. However, the good news is that any transportation organization or a regular person with a GPS receiver can access this data freely.
This technology has become an essential tool used in many solutions for the logistics industry. It's easy to use and helps companies to optimize their operations and improve efficiency. Here are some examples of how GPS tracking software can be used in logistics.
Fleet management. Companies can monitor the location and performance of their vehicles in real-time to optimize routes, reduce fuel consumption, and ensure that drivers are adhering to safety regulations.
Delivery tracking helps logistics companies' clients track their real-time delivery progress. It improves transparency and customer satisfaction:
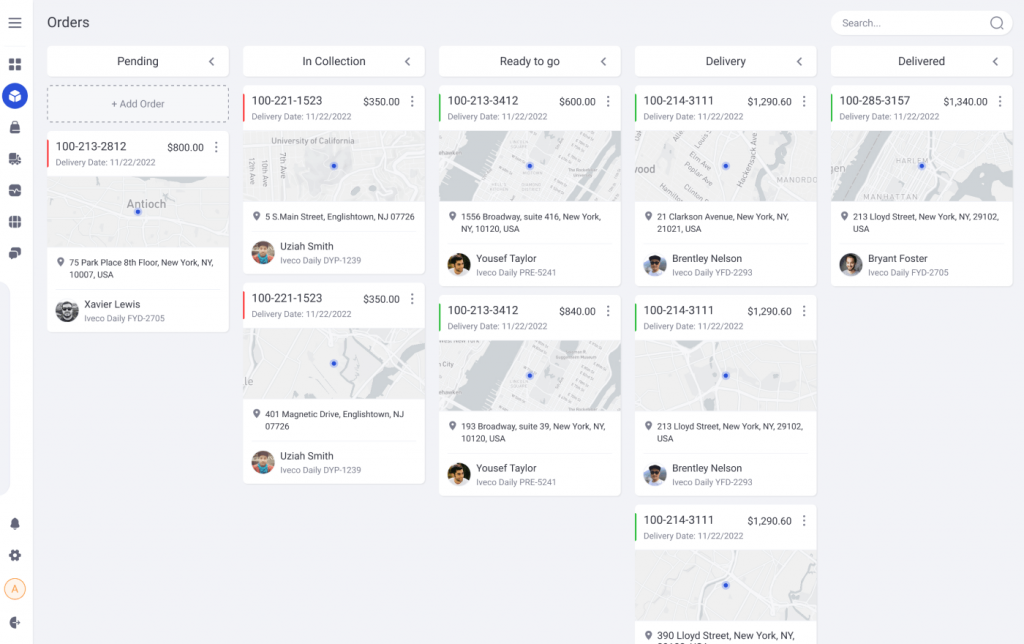
Source: Delivery Management System
Inventory management solutions for logistics companies can monitor the location and movement of inventory. Such an approach helps to optimize warehouse operations and ensure that inventory is stored and transported efficiently.
Asset tracking. Here, GPS tracks the location and movement of valuable assets such as equipment, vehicles, and trailers. This way, companies can prevent theft and loss and optimize their assets' use.
GIS, or Geographic Information Systems, is the embodiment of modern approaches to mapping. Solutions based on this tech are in high demand, not only among organizations working in logistics and transportation. Anybody needing quick access to various data sets related to specific locations on the map can rely on such systems.
GIS solutions can provide access to cartographic, photographic, digital data or spreadsheets, according to their specific purpose. For example, cartographic data can include population density or survey results, which is helpful for those involved in social sciences. Digital data regarding the location of towns, warehouses, gas stations, and other objects can be gathered from satellites and included in GIS maps.
In order not to get lost in the abundance of information, users can, so to say, dig deeper in a given area. GIS allows quick switching between different data layers following the current user needs. By pointing to a specific spot on the map, users can get immediate access to related information. For example, one can use a mobile solution to tap on a particular warehouse to check how full it is and how many vehicles are currently available nearby.
Read Also What Yard Management Systems Are and How They Can Help Your Logistics Business
Quick access to rich datasets that GIS maps provide via an intuitive web application can bring multiple benefits. Now, let's see examples of how custom-made logistics software can be used in practice.
Using GIS Solutions in Logistics and Transportation
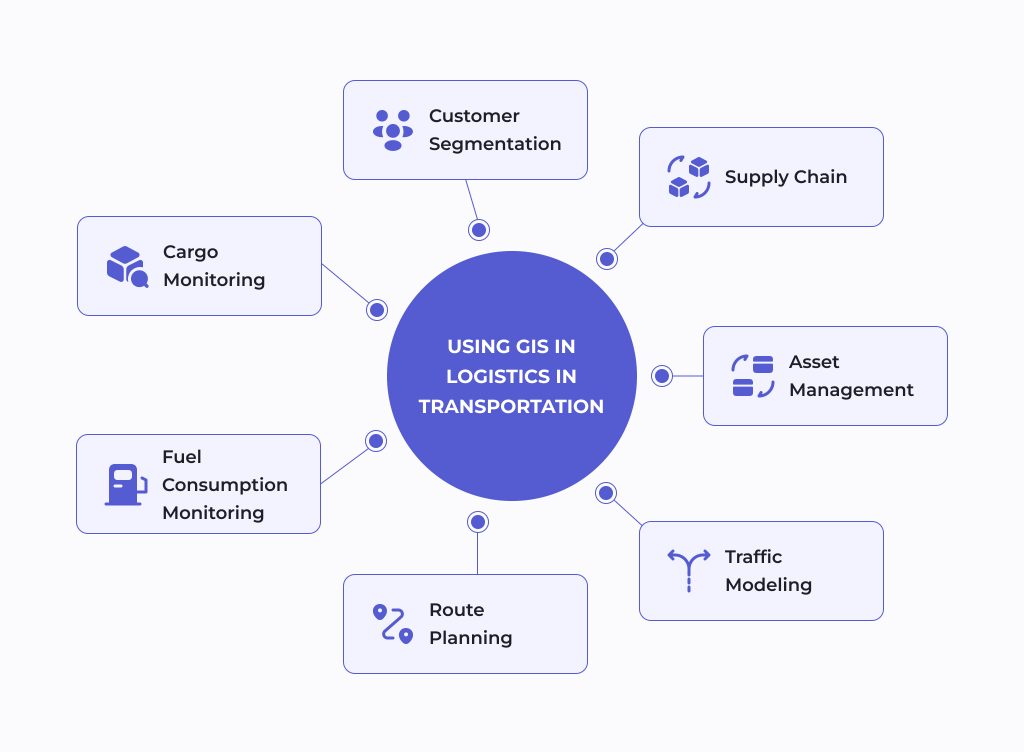
Customer Segmentation. One of the most essential factors in the success of any logistics or transportation business is understanding the customers. Companies can use GIS maps to segment their customer base by location, demographics, and other factors. This info can be visualized as heat, category, or clasper maps.
Supply Chain. GIS maps can be used to analyze and optimize the entire supply chain, from raw materials to finished products. By mapping the flow of goods and materials, you can identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks and make strategic decisions to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of your supply chain. GIS solutions can provide access to vehicle capabilities, customers' and intermediaries' availability time windows, and other information required for building the most efficient routes and schedules.
Asset Management. GIS solutions enable logistics and transportation businesses to monitor their assets' location and condition in real-time. Replacing your equipment before its approximated fatigue degree reaches a critical value may significantly reduce maintenance costs. Besides, unplanned equipment failure harms your customer relationships since your logistics and transportation organization fails to make deliveries on schedule.
Traffic Modeling. GIS solutions can be used to model and predict traffic patterns, essential for route planning, delivery scheduling, and optimizing fleet management. City planners and transportation authorities can also use this information to plan and design roads, highways, and public transportation systems.
Route Planning. GIS maps can be used to optimize delivery routes based on factors such as traffic, road conditions, and delivery priorities. It helps reduce travel time, improve delivery accuracy, and minimize fuel consumption.
Fuel Consumption Monitoring. In logistics and transportation, fuel is one of the most significant expenses. GIS maps can monitor fuel consumption and identify areas where fuel efficiency can be improved. For example, it helps determine how idling time can be reduced and ensure that vehicles are well-maintained and operate efficiently. As a bonus to improved cost-effectiveness, logistics and transportation businesses can prolong the life of their vehicles.
Cargo Monitoring. GIS helps track the location and movement of cargo in real time. It's vital to ensure that deliveries are made on time and in good condition. This information can also be used to prevent theft and loss and optimize cargo space use.
Conclusions
The complexity of logistics and transportation in the modern world requires more than tracking the movement of vehicles. It's also essential to add some context to this information. GIS solutions can operate both historical and real-time data to enable access to the big picture. Logistics companies can use historical data to make informed decisions and quickly make changes following new data on recent events. GIS solutions have a layered data structure that allows switching between different types of information related to the same region. It enables different departments of the logistics company to use a single system for solving various challenges.
