What’s a Data Governance Framework and How to Implement One for Your Business
The flow of organizational data must not be left uncontrollable. When information flows ceaselessly across vast digital networks, companies face an ever-growing challenge in managing and safeguarding their valuable assets. The exponential growth of business data, increasing regulatory requirements, and evolving consumer expectations have necessitated the use of data governance frameworks. They serve as essential roadmaps, guiding businesses toward responsible data practices while ensuring transparency, compliance, and trust. Today, we'll consider their main features and learn how you can build such a framework for your business.
Importance of Data Governance
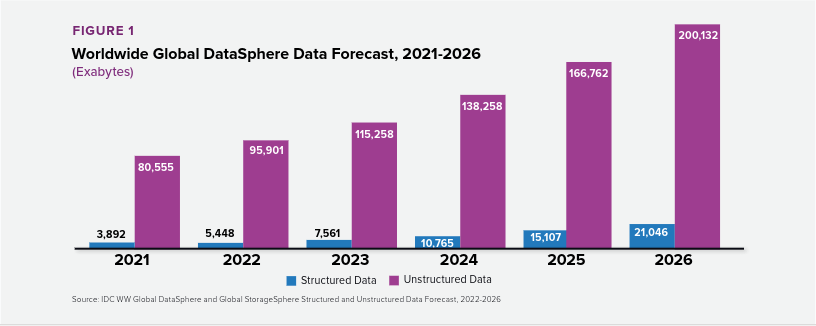
As the IDC's Global DataSphere report [PDF] forecasts, the amount of data created annually will grow to more than 221,000 exabytes by 2026. An exabyte is 1,000 petabytes, by the way. It leads to the need to reconsider data management habits both on global and local levels. Adopting data governance frameworks is one of the options.
Let’s deal with terms first. Data governance can be described as the framework of policies, processes, and guidelines that dictate how a business organization collects, manages, protects, and utilizes its data assets. It establishes the rules of engagement, ensuring that business data is reliable, accurate, accessible, and secure throughout its lifecycle. Business specifics dictate which type of information should be controlled.
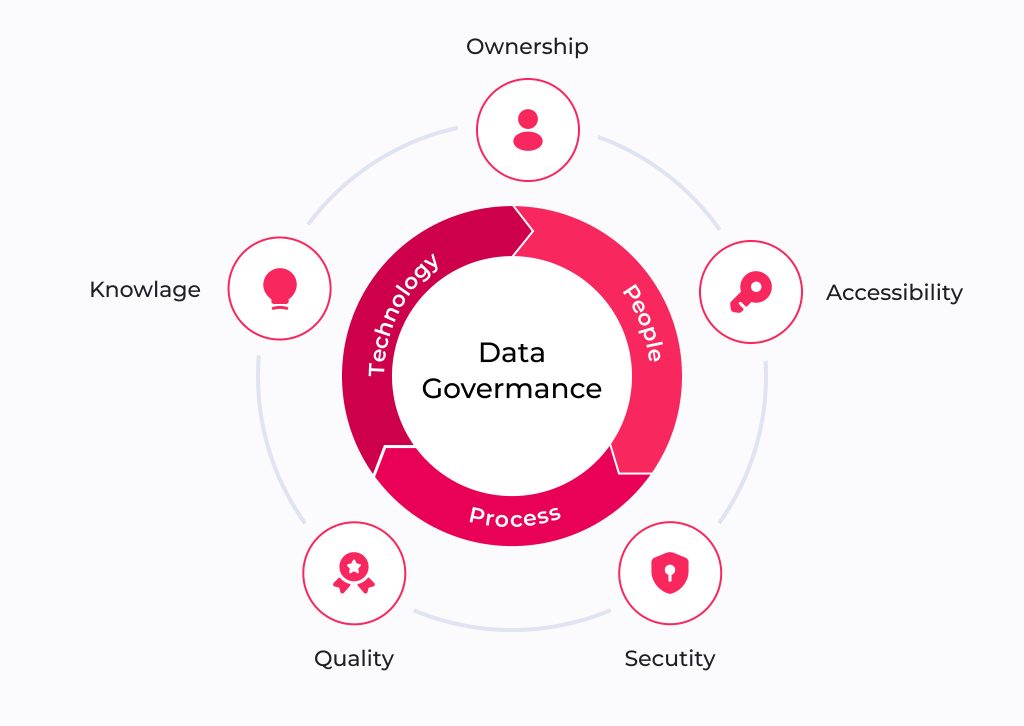
For example, a logistics company might need to adopt a data governance framework to ensure the safety of its client's sensitive information and enable access to accurate warehouse data to all interested departments. At its core, data governance empowers businesses to establish a robust foundation for decision-making, allowing them to harness the full potential of their data while mitigating risks.
Data Governance Benefits
Unleashing data's potential. Businesses can transform their data into a strategic asset by implementing a well-structured data governance framework. Clear guidelines and standardized practices enhance data quality, enabling companies to derive meaningful insights and make informed decisions. With trustworthy and reliable data at their fingertips, leaders can unlock opportunities for innovation, drive operational efficiencies, and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Ensuring compliance and mitigating risks. In an era of heightened data protection regulations, such as California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) or the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), data governance frameworks serve as a shield against legal and regulatory pitfalls. With defined data governance policies, businesses can align their practices with relevant laws, ensure the protection of sensitive information, and safeguard customer trust.
Fostering collaboration and accountability. Data governance fosters a culture of collaboration and accountability within business organizations. Establishing clear ownership and responsibility for data breaks down silos and promotes cross-functional cooperation. With data governance frameworks in place, employees at all levels have a shared understanding of data-related processes, roles, and responsibilities, ensuring consistent and reliable information across departments.
Read Also Dangers of Data Silos And Efficient Strategies for Eliminating Them
Building customer trust. In an age where privacy breaches and data misuse dominate headlines, customer trust has become a critical differentiator. A robust data governance framework inspires confidence among consumers by ensuring that their personal information is handled with care, respect, and compliance. Businesses can build stronger, long-lasting customer relationships by prioritizing data protection, fostering loyalty, and positioning themselves as ethical and responsible data stewards.
Implementing Data Governance Frameworks
Data Governance Roles and Responsibilities
First, it's essential to understand the major roles and responsibilities involved in implementing data governance frameworks. The content of such a list may vary. It depends on the features of your business and the organization's size, but it usually will include the following.
The Chief Data Officer (CDO) is the visionary leader responsible for setting the strategic direction and overseeing the organization's data management initiatives. The CDO collaborates with executive leadership to define data governance goals, align them with business objectives, and establish policies and guidelines for data management.
Data owners are usually business unit heads or senior executives. They hold the ultimate accountability for specific sets of data within an organization. These stakeholders deeply understand the data's context, purpose, and value and act as custodians of data assets.
Data stewards are responsible for the day-to-day implementation and execution of data governance policies and procedures. They perform data classification, metadata management, and monitor business data quality and accuracy.
Data governance committees serve as the collective driving force behind the organization's data governance strategy. These committees typically consist of representatives from different business units and functions, including IT, legal, compliance, and privacy. Their primary objective is to ensure cross-functional collaboration and decision-making, promoting a holistic and inclusive approach to data governance.
Data Governance Tools
To make implementing a data governance framework more efficient, you should rely on efficient tools to harness the business data.
Data catalogs serve as central repositories that capture and organize metadata, providing a comprehensive inventory of an organization's data assets. These tools offer a holistic view of data lineage, relationships, and usage, enabling users to discover and understand available data resources. With robust search and tagging capabilities, data catalogs facilitate data exploration, reduce redundancy, and promote data reuse, saving time and resources.
Data quality management tools are always at hand when you need to ensure business data accuracy, completeness, consistency, and integrity. These tools employ a range of functionalities, such as data profiling, data cleansing, data validation, and anomaly detection, to identify and resolve data quality issues. By establishing data quality rules and metrics, organizations can measure and monitor the quality of their data over time, enabling proactive data management and driving confident decision-making.
Data visualization solutions transform complex datasets into visually appealing and intuitive representations such as charts, graphs, and interactive dashboards. By presenting complex business data visually compellingly, these tools allow stakeholders to grasp complex patterns, trends, and correlations quickly. Such solutions empower users to explore and analyze data, gain actionable insights, and communicate findings effectively:
Source: A Comprehensive Economic Research Tool with Data Visualization Features
Data security and privacy tools encompass a range of technologies, including data encryption, access controls, masking, and anonymization. Such software solutions can help businesses establish and enforce data security policies, safeguard sensitive data, and comply with regulations.
Read Also Using Dynamic Tables for Advanced Data Modeling and Analysis
Bring it All Together
Step 1: Define the data governance objectives and scope. Identify the key drivers for data governance within your business organization, whether it's enhancing data quality, improving compliance, enabling data-driven decision-making, or all of the above. A clear vision and mission statement sets the foundation for the entire data governance initiative and ensures alignment with organizational goals.
Step 2: Assemble a data governance team. You already know what the major roles in data governance frameworks are. Now, it’s time to build a cross-functional data governance team according to these roles. The team should include representatives from business units, IT, legal, compliance, and data management functions.
Step 3: Conduct a data assessment and inventory. Perform a comprehensive data assessment to understand the organization's data landscape deeply. Identify critical data assets, their sources, usage, and quality. Conduct a data inventory to capture metadata, data lineage, and relationships. It'll help to provide insights into data gaps, redundancies, and areas requiring improvement, serving as a baseline for future data governance activities.
Step 4: Develop data governance policies that follow the defined objectives and assessment results. These policies should encompass data quality standards, classification, security, privacy guidelines, and compliance requirements.
Step 5: Implement data governance processes and procedures. Translate what you understand on the previous stage into actionable processes and procedures. You should establish procedures for data issue resolution, data change management, and data documentation. It'll help to achieve a systematic approach, ensuring consistency and efficiency.
Read Also: Don’t Let Your Data Get Rusty. The Importance of Legacy System Integration
Step 6: Enable data governance tools and technologies. We've already mentioned software solutions that can be pretty helpful for your business if you decide to implement a data governance framework. Here, you can leverage them to streamline and automate the processes.
Step 7: Establish communication and training programs. Develop a communication plan to raise awareness, share progress, and emphasize the importance of data governance. Conduct training programs to educate stakeholders on data governance principles, processes, and tools.
Step 8: Monitor, evaluate, and evolve. Establish a robust monitoring and evaluation framework to assess the effectiveness of the data governance program. Continuously measure key performance indicators (KPIs) such as data quality, compliance levels, and user adoption. Conduct regular audits to identify areas for improvement and address emerging data governance challenges. Evolve the data governance framework based on insights and feedback, ensuring its relevance and alignment with evolving organizational needs.
Conclusions
Data requires as much attention and effort as any material asset your company possesses. Whether you buy a new vehicle for your delivery business or collect customer data via the CRM system, there should be processes and procedures in place to monitor them until the day of their disposal. Data governance frameworks provide simple answers on what, how, and by whom should be done to get the most out of your data.
